Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Understand Addition As Putting Together And Adding To, And Under- Stand Subtraction As Taking Apart And Taking From.
K.OA.A.2
Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to represent the problem.
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Add And Subtract Within 20.
1.OA.C.6
Add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction within 10. Use strategies such as counting on; making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 + 4 = 14); decomposing a number leading to a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9); using the relationship between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12, one knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7 by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13).
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Work With Addition And Subtraction Equations.
1.OA.D.8
Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 + ? = 11, 5 = ? – 3, 6 + 6 = ?.
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Represent And Solve Problems Involving Addition And Subtraction.
1.OA.A.1
Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.*
*See Glossary, Table 1.
Example Task
1.OA At the Park
Task
- There were 7 children at the park. Then 4 more showed up. How many children were at the park all together?
- There were 7 children at the park. Some more showed up. Then there were 11 children in all. How many more children came?
- There were some children at the park. Four more children showed up. Then there were 11 children at the park. How many children were at the park to start with?
Solution
Students may use objects, pictures, or equations to represent their solutions. The solutions show equations with a question mark representing the unknown value, but other symbols are often used. For example, 4 + ? = 11 might also be written
4 + ____ = 11 or 4 + ☐ = 11.
- Total Unknown: There were children in all.
Possible equation: ? - Addend Unknown: more children came.
Possible equation: ? - Start Unknown: There were children in the park to start with.
Possible equation: ?
Progressions
- In a Compare situation, two quantities are compared to find "how many more" or "how many less."
- Addition and Subtraction Situations by Grade Level
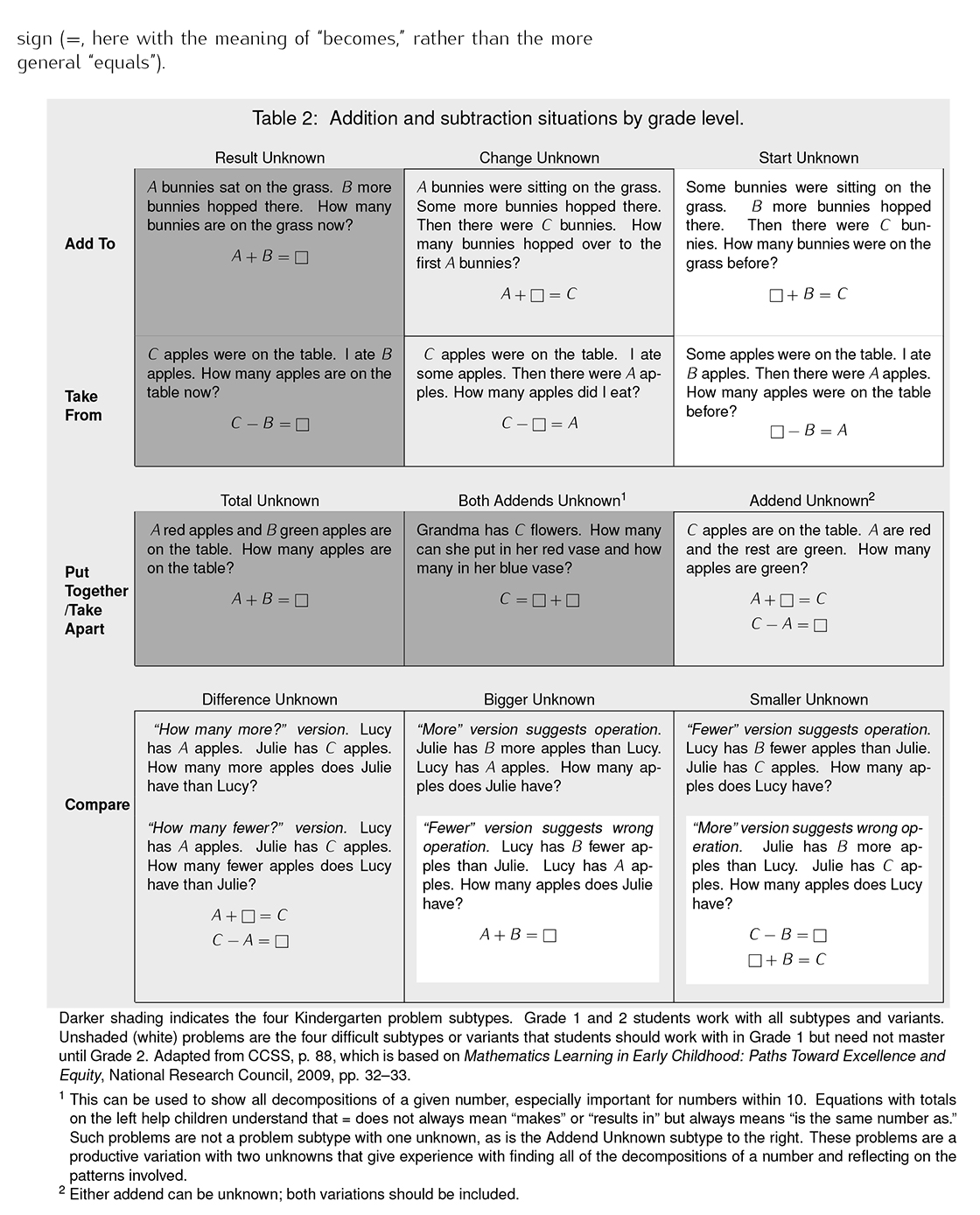
Please reference pages 9 and 12 in the Progression document
Tasks
Focus
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Add And Subtract.
1.NBT.C.4
Add within 100, including adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number, and adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used. Understand that in adding two-digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose a ten.
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Add And Subtract Within 20.
2.OA.B.2
Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies.* By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers.
*See standard 1.OA.6 for a list of mental strategies.
Measurement And Data
Represent And Interpret Data.
1.MD.C.4
Organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories; ask and answer questions about the total number of data points, how many in each category, and how many more or less are in one category than in another.
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Represent And Solve Problems Involving Addition And Subtraction.
1.OA.A.2
Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Represent And Solve Problems Involving Addition And Subtraction.
2.OA.A.1
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.*
*See Glossary, Table 1
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Angle And Measure Angles.
4.MD.C.7
Recognize angle measure as additive. When an angle is decomposed into non-overlapping parts, the angle measure of the whole is the sum of the angle measures of the parts. Solve addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems, e.g., by using an equation with a symbol for the unknown angle measure.